目的 通过与DAS28比较,探讨能量多普勒评价类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis ,RA) 疾病活动度的价值。方法 选择RA患者74例,记录膝关节的能量多普勒信号,并记录28个关节的肿胀数、压痛数、血沉(erythrocyte sedimentation,ESR)、C-反应蛋白(CRP)及患者基于100 mm视觉模拟尺(VAS),对疾病活动度进行评价,计算DAS28评分。专业超声医师对患者肿胀膝关节进行能量多普勒检查,PD评分分为4级后与DAS28评分做Kappa检验。结果 74例中,1例(1%)无血流信号,2例(3%)少量点状信号,32例(43%)大量短条状血流信号,39例(53%)树枝状信号。将DAS28-CRP及DAS28-ESR分组后与能量多普勒信号分别比较发现,能量多普勒与DAS28一致性好(DAS28-ESR κ=0.701, P<0.05;DAS28-CRP κ=0.777, P<0.05)。结论 能量多普勒能够评价RA关节炎的疾病活动度。
Objective To compare the correlations between power Doppler and Disease Activity Score with 28 joints (DAS28) by estimating the value of the activity of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).Methods Seventy-four cases of RA patients were selected. The power Doppler signals of knee joints were recorded. The number of cases of swelling of 28 joints, the number of cases of tenderness of the 28 joints, erythrocyte sedimentation(ESR) and C-reactive protein(CRP) were recorded. The patients were evaluated according to the 100mm visual analogue scale (VAS) in order to calculate the DAS28 score. According to the intensity of signals, the ultrasound doctor performed a power Doppler examination on the swollen knees of the patients and divided them into four groups.Results A total of seventy-four patients with RA were enrolled, including one knee (1%) without blood flow signals, two patients (3%)with a small number of punctate signals, thirty-two cases (43%) with a large number of short-striped blood flow signals and thirty-nine cases (44%) with dendritic signals. A comparison with signals of power Doppler revealed that power Doppler well conformed to DAS28 (DAS28-ESR κ=0.701, P<0.05;DAS28-CRPκ=0.777, P<0.05).Conclusions The disease activity of RA can be evaluated with power Doppler.
类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis, RA), 是一种以关节滑膜炎为特征的自身免疫病[1], 可以侵犯全身大小关节, 影响患者的日常生活能力。在RA的治疗中, 常使用DAS28[2]评价疾病活动度制定治疗方案, 但DAS28计算复杂且受多种因素的影响。肌肉骨骼超声检查是应用于风湿病领域的新兴方式[3], 可以检测关节局部情况, 且简便易行[4, 5, 6]。本研究通过与DAS28评分比较, 探讨能量多普勒评价类风湿关节炎疾病活动度的价值。
选择2014-10至2017-03在我院风湿科住院RA患者74例, 符合1987年ACR RA分类标准或ACR/EULAR 2010年RA分类标准, 膝关节症状较明显, 其中女57例, 男17例, 年龄20~78岁, 平均(51.73± 14.73)岁。
记录所有患者的性别、年龄等一般资料。(1)评估各项临床疾病活动指标, 包括疼痛评分[采用100 mm视觉模拟评分法(VAS)]、28个关节(双手近端指间关节、双手掌指关节、双腕、双肩及双膝)的肿胀关节数(SJC)和28个关节的压痛关节数(TJC), 由同一位风湿专科医生进行评估。(2)实验室指标:检测ESR、CRP。(3)疾病活动度以DAS28-ESR、DAS28-CRP进行评价。其中DAS28计算公式[7]为:DAS28(CRP)=0.56× (TJC28)1/2+0.28× (SJC28)1/2+0.014× GH+0.36× ln(CRP+1)+0.96; DAS28(ESR)=0.56× (TJC28)1/2+0.28× (SJC28)1/2+0.014× GH+0.70× ln(ESR)。病情稳定分为0级至3级, 0级< 2.6, 低活动度为1级 2.6-3.2, 中度活动为2级 3.2-5.1, 高度活动为3级> 5.1。
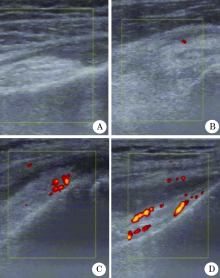
检测仪器采用美国GE公司LOGIQ e, 探头型号及中心频率为12 (8~13) MHz。由同1名经过正规肌骨超声培训的风湿科医师应用能量多普勒超声检查RA患者症状较著的单侧膝关节。据能量多普勒(PD)血流信号强弱进行半定量评分[3]:其中0为无滑膜血流信号, 1为少量点状血流信号< 1/3滑膜面积; 2为大量短条状血流信号≥ 1/3滑膜面积, 且< 2/3滑膜面积; 3为树枝状信号≥ 2/3滑膜面积。
PD评分分为4级后与DAS28评分做Kappa检验, 对比DAS28活动度(0-3级)及PD评分(0-3)的一致性。κ ≤ 0.2一致性水平差, 0.2< κ ≤ 0.4一致性一般, 0.4< κ ≤ 0.6一致性中等, 0.6< κ ≤ 0.8一致性好, κ 大于0.8一致性非常好。
使用SPSS 17.0软件, 计量数据以
据PD血流信号强弱, 其中0级1例; 1级2例; 2级32例; 3级39例(图1)。
DAS28-ESR与PD分级比较, 同为0级的为1个, 1级的1个, 2级的28个, 3级的32个, 计算κ =0.701, P< 0.05。DAS28-CRP与PD分级比较, 同为0级的1个, 1级的1个, 2级的30个, 3级的33个, 计算κ =0.777, P< 0.05。说明该研究的一致性水平好。
肌肉、骨骼超声近年已成为诊断、评估类风湿关节炎疾病活动及疗效的重要手段之一[8, 9], 已有关于超声诊断、评估生物制剂疗效的研究报道, 但是使用能量多普勒评价RA活动度的研究仍然很少。目前, 类风湿关节炎要求达标治疗, 低疾病活动度或病情稳定的评价显得尤为重要, 这就要求临床能够快速评价患者病情, 以制定治疗方案, 能量多普勒的快捷准确在此非常重要。
类风湿关节炎的病理变化为滑膜渗出、增生伴滑膜血管翳生成[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15], 关节内滑膜血管的过度增生是RA滑膜增生活跃的标志[10]。而能量多普勒超声可以监测到过度增生的滑膜血管翳内的血流。本研究中发现, RA患者DAS28-CRP及DAS28-ESR与PDUS相比较一致性好(P< 0.05), 表明PDUS同DAS28-CRP及DAS28-ESR均可以评价RA的病情活动度。李拾林等[16]对34例RA患者的30个关节研究后发现, DAS-28评分、ESR、CRP与超声滑膜炎、PDUS评分之间均存在非常显著的相关性(P< 0.001)。Geng等[17]对111例RA患者的22个关节进行用药前后超声研究, 发现PDUS与SJC、TJC、ESR、CRP、 DAS28-CRP、DAS28-ESR及CDAI、SDAI等均存在相关性。田静等[18]对56例RA患者的28个关节研究时也发现, 超声PD评分与RA疾病活动性指标DAS28、CRP及ESR高度相关。也有报道使用PD评价生物制剂治疗后的RA的病情活动度[19, 20, 21]。
上述研究均为研究多个关节与RA的疾病活动度, 且多为小关节, 临床操作中费时, 对超声仪器及探头的要求高。本研究较上述研究增加了样本量, 并且直接对症状较明显的单关节大关节— — 膝关节进行超声检查, 节省了时间, 放宽了对超声机器及探头的要求。本研究仍有不足之处, 血沉及CRP设有上限, 会影响关节肿痛数较少的患者DAS28评分及分组; PD与操作人员的经验及机器参数设置有关。
总之, 本试验通过研究DAS28-ESR、DAS28-CRP与PD之间的关系, 发现能量多普勒有评价类风湿关节炎病情活动度的价值。
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|